Disc herniation is a common cause of neck and low back pain. Terms to describe disc problems include bulging, ruptured, slipped, or extruded. Sometimes a disc herniation occurs spontaneously or incidental to injury, repetitive movements, or degenerative disc disease.
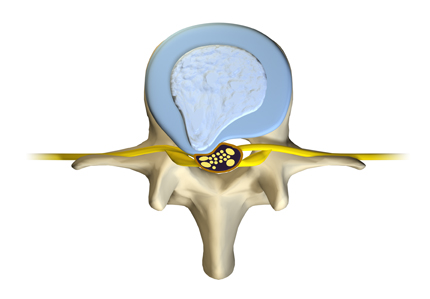
The intervertebral discs serve as your spine’s shock absorbers. Each disc is composed of a sturdy tire-like annulus fibrosis that encases a gel-like interior called the nucleus pulposus. Endplates anchor each disc in place between two vertebral bodies.
Growing older, trauma, injury, smoking, poor diet, being overweight, and wear and tear can alter disc strength, resiliency and structural integrity.
What are typical symptoms?
Why see a spine specialist for a diagnosis?
What are the treatment options?
What happens
The annulus fibrosis—the protective band of tissue protecting the nucleus pulposus—cracks, tears, or breaks open. This allows some of the gel-like nuclear material to ooze outside the disc. A bulging disc—the nucleus pulposus remains contained within the disc—may be a precursor to herniation. Escaping disc matter may cause:
- Nerve root compression
- Spinal canal compression
- Both
Symptoms
Pain is the foremost symptom of a herniated disc. The disc material, and potential loss of disc height, compresses the spinal nerves, cord and/or canal. Furthermore, within the escaping disc matter is a chemical irritant that causes nerve inflammation and pain. Neck or back pain may spread into your arms or legs. Cervical radiculopathy and sciatica (lumbar) are examples.
| Cervical Disc Herniation | Lumbar Disc Herniation |
| Neck pain, mild to intense | Low back pain, mild to intense |
| Upper extremity pain, weakness | Buttock, leg pain and/or weakness |
| Hand clumsiness | Difficult and painful to walk, stand, bend forward, backwards, side-to-side |
| Movement increases pain | Movement increases pain |
| Neck, Shoulders, Arms, Hands | Low Back, Buttocks, Legs |
| Sensations: burning, tingling, numbness, pins and needles | Sensations: burning, tingling, numbness, pins and needles |
| Rare, bladder and bowel dysfunction | Rare, bladder and bowel dysfunction |
Accurate diagnosis
Consult an expert, especially if neck or back pain develops suddenly, quickly worsens, or you have a pre-existing spinal disorder. An accurate diagnosis is essential to an effective and successful treatment plan.
Your medical history and physical and neurological examinations are very important. You and your doctor discuss your symptoms, when they developed, and treatments tried. The doctor tests your reflexes and evaluates you for muscle weakness, loss of feeling, and signs of neurological injury.
Diagnostic tests help the doctor confirm which disc (or discs) is damaged. A simple spinal x-ray can show collapsed disc space. CT and MRI are sensitive imaging tools that detail bone, disc and nerve structures.
Treatment options
Non-surgical treatment often helps to relieve pain and symptoms. Your doctor may combine two or more therapies to maximize the success of your treatment.
Non-surgical treatments
- Activity modification
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Pain medication (a narcotic, painkiller)
- Muscle relaxing medication
- Spinal injection
- Short-term bracing supports the spine, may help relieve pain
- Physical therapy
- Acupuncture
When your surgeon may discuss surgical treatment
- Spinal instability
- Neurologic dysfunction
- Pain and symptoms are unrelenting
- Non-operative treatment fails and pain persists
Surgical treatment
You may be a candidate for a minimally invasive spine surgery. Sometimes spinal stabilization and fusion are necessary to stop the spine from moving or help alleviate progression of symptoms.
Keep in mind that spine surgery is not always necessary. However, if your surgeon discusses surgical options with you, be assured his recommendation is made with the greatest concern to your healthcare.




